

|
 | ||
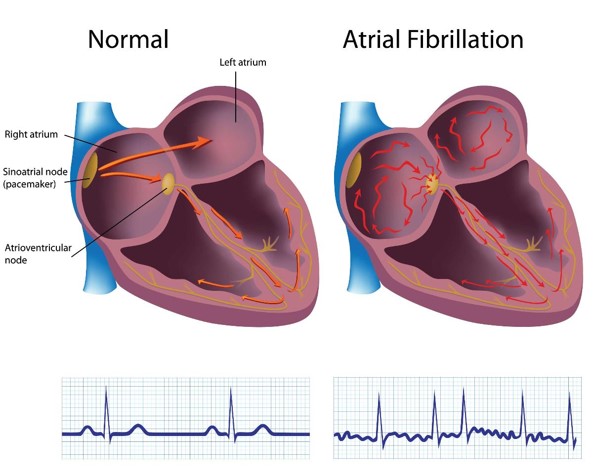
Atrial fibrillation (AF) | ||
 |
 |
Atrial fibrillation is the most common persistent arrhythmia. The incidence of atrial fibrillation continues to increase with aging, and the peak incidence is over 65 years old, which can be as high as 10% in people over 75 years old. Atrial fibrillation is characterized by an irregular, usually rapid heart rate, which can increase the risk of stroke, heart failure and other heart related complications. In atrial fibrillation, the two upper chambers (atrium) of the heart beat irregularly, the atrium lost its effective systolic function, and the two lower chambers (ventricles) of the heart did not coordinate. Atrial fibrillation patients are usually flustered, shortness of breath, headache, dizziness, chills, and even limb weakness, lower limb edema. According to incomplete statistics from WHO, there are nearly 40 million AF patients in the world, and there is an increasing trend year by year. At present, there are more than 10 million patients with atrial fibrillation in China, and also more than 10 million patients in the United States and Europe. |
| Risks of Atrial Fibrillation | ||
 |
 |
Atrial fibrillation not only causes heart failure, exacerbates myocardial ischemia and triggers myocardial infarction, but also makes atrium lose its contractile function and blood accumulate in atrium to form thrombus. After atrial thrombus falls off, it flows to different parts of the body with blood. The most serious risk is to induce stroke by cerebral embolism. Therefore, atrial fibrillation greatly increases the mortality of the elderly, so the early treatment of atrial fibrillation is very important. |
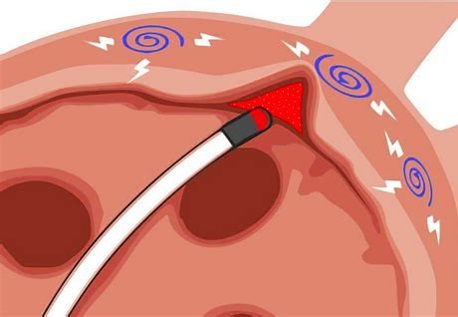
| Treatment of atrial fibrillation | ||
 |
 |
There are four aspects in the treatment of atrial fibrillation:
|
| Currently, the antiarrhythmic drugs used in the treatment of atrial fibrillation include propafenone, flecainide, dofetilide, sotalol, amiodarone, etc.; however, there are some problems in the treatment of AF with these antiarrhythmic drugs. The treatment of atrial fibrillation is a complex clinical issue; therefore, Atrial Fibrillation Center has been established in China to specialize in exchanging experience and knowledge for the diagnosis and treatment of atrial fibrillation. | ||
| Problems in Anti-atrial Fibrillation Drug Therapy | ||
 |
 |
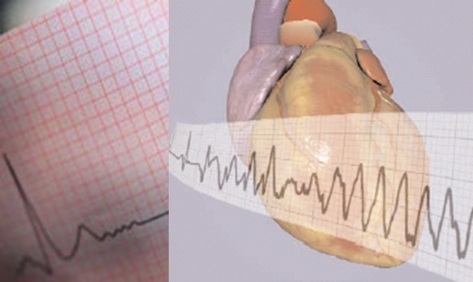
Although the clinical antiarrhythmic drugs (sotalol, dofetilide, amiodarone, etc.) are effective for atrial fibrillation, they lack atrial selectivity. Therefore, the treatment of atrial fibrillation can cause prolonged ECG QT interval, TdPs, ventricular arrhythmia or ventricular fibrillation (left figure).
|
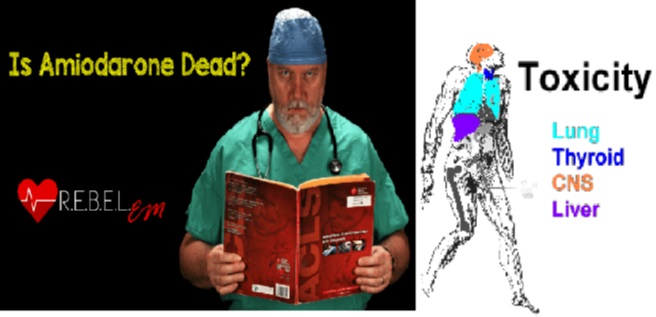 http://rebelem.com/is-amiodarone-dead/ |
For example, the most effective drug amiodarone in the treatment of atrial fibrillation, in addition to prolonging the ECG QT interval, has the risk of causing ventricular arrhythmia, also other side effects, e.g. hepatotoxicity, pulmonary fibrosis, thyroid dysfunction, etc. (left figure). | |
Therefore, there is a lack of ideal drugs with selective inhibition of atrial specific ion channels in clinic (which can inhibit atrial rhythm disorder and terminate atrial fibrillation without inducing ventricular arrhythmias and other side effects) to treat atrial fibrillation. Our innovative products AMZ001、AMZ002 selectively inhibit atrial specific potassium channels and effectively prevent and terminate atrial fibrillation. They belong to Class I atrial-selective anti-atrial fibrillation drugs. | ||